81 Tagore Lane, TAG A, #01-11 Singapore 787502 ♦ Reservation : +65 6727 5599
Are Liver and Kidney Safe to Consume During Postpartum?
Organ meat is commonly recommended to avoid during pregnancy as it is deemed unsafe due to high levels of Vitamin A which can potentially cause Vitamin A toxicity, so why is it commonly available in traditional confinement foods? Let’s find out!
Types of vitamin A (retinol vs beta-carotene)
In general, there are two types of Vitamin A which are preformed Vitamin A and provitamin A. Preformed Vitamin A is also known as Retinol whereas provitamin A is also known as beta-carotene.
One of the main differences is that retinol is from animal sources like eggs, liver, kidney, or beef whereas beta-carotene is from plant sources like carrot, pumpkins, goji berries, or red spinach.
Vitamin A from animal sources has higher bioavailability than plant sources. That is why the prevalence of Vitamin A deficiency is higher in lower economic countries such as those in South Asia like Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, Pakistan, and India where their diet is mainly plant-based.
What is the role of vitamin A during confinement?
According to the recommended dietary allowance of Singapore, Vitamin A (Retinol equivalents) recommendations become even higher during lactation as compared to pregnancy.
| Non-Pregnant Women | Pregnant Women | Lactating Women |
| 750mcg/day | 750mcg/day | 1200mcg/day |
Many research has discussed how vitamin A in breast milk is heavily dependent on maternal’s adequate intake. Breast milk is only rich in vitamin A if there is sufficient vitamin A in the mother’s liver and breast in preparation for lactation.
Besides that, colostrum has a higher vitamin A concentration compared to transitional milk and mature milk. This also shows that prolonged lactation reduces body stores of the vitamin.
Why is vitamin A important for infants? It is crucial for infant growth, vision, immune system development, and prevention of infection. As for mummies while recovering during confinement, skin and muscles that are stretched would also need to contract and recover. There would also be wounds that need to be recovered.
Therefore, collagen production during this time is important. Along with iron, copper, protein, and zinc, Vitamin A would also play a part in building collagen.
Toxicity, upper limit of vitamin A
The upper limit of Vitamin A intake as according to the Institute of Medicine during lactation is 3000mcg of preformed Vitamin A per day. This is important as it gives a guide to limit your risk of toxicity of Vitamin A as too much of Vitamin A may cause hepatotoxicity.
Toxicity in infants and children varied widely such as skeletal abnormalities, bone tenderness and pain, increased intracranial pressure, desquamation, brittle nails, mouth fissures, alopecia (hair loss), fever, headache, lethargy, irritability, weight loss, vomiting, and hepatomegaly (enlarged liver beyond its normal size).
Too much Vitamin A during pregnancy, may potentially cause birth defects. One other theory is that too much Vitamin A could potentially be linked to postpartum depression. This is because research found breast milk is rich in Vitamin A, especially during the first few weeks. It is found that the quantity of vitamin A transferred to the infant via exclusive breastfeeding would be sufficient to cause acute Vitamin A intoxication if consumed by an adult. It is hypothesized that thus mothers who choose to not breastfeed or have early cessation of breastfeeding are at higher risk of postpartum depression due to the retention and accumulation of retinoids in the brain and other tissues that would normally be transferred to the infant for nutrition.
Food safety, appropriate portions, frequency
Traditional confinement foods include organ meats. As a matter of fact, we know grandmothers and aunties who swear by having plenty of organ meats during our confinement. It does have a distinctive and acquired taste. Not many of us enjoy having organ meats but we eat them anyway because we understand that our mothers-in-law, mothers, and grandmothers do have the best of intentions for our well-being after childbirth.
Knowing all that is discussed above, we also know that the liver is the biggest source of preformed vitamin A. So, is it safe for mummies to eat foods like pork kidney and pork liver in the diet after childbirth? Is it helpful or harmful? According to Singapore food Composition estimated nutritional values, preformed Vitamin A in organ meats are stated in the table below:
| 100g Raw Weight | Preformed Vitamin A Content, mcg (UL:3000mcg) |
| Pork Liver | 4972 |
| Pork Kidney | 741 |
Chinese Nutrition Society Guidelines for breastfeeding mothers in China recommended intakes of organ meats like 85g pork liver 1 to 2 times per week. On the other hand, there are no specific guidelines on organ meat intakes in Singapore dietary guidelines, but the general recommendation for such foods in moderation with a balanced diet that has adequate fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein is fine, assuming no additional vitamin A supplementation is being taken by mummies who are breastfeeding.
How TWSG serves
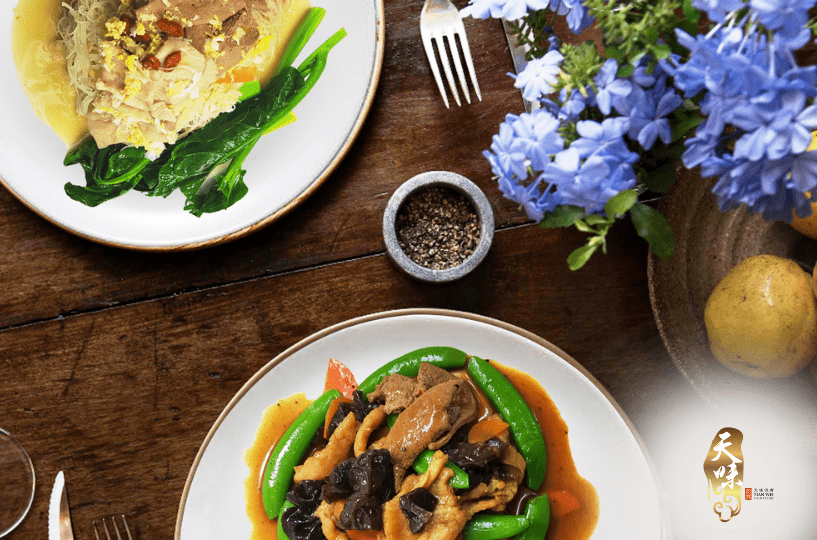

With respect to traditional dietary confinement customs, Tian Wei Signature menu, organ meats are served. Both vitamin-A-rich sources from plants and animals are incorporated into the menu, this means both retinol and beta-carotene-rich food sources.
Due to the increased requirements of Vitamin A to support wound recovery and the demands of breastfeeding while still minimizing the risk of Vitamin A toxicity, Tian Wei Signature’s dietitian, Eunice Tan looks into these key issues in a postpartum diet and key nutrients in the menu to ensure that foods like organ meats are only served one to two times per week as per guidelines in small portions.
Some of the delicious confinement meal prepared for mummies throughout the 28 days menu are:
- Braised White Vermicelli with Pork Liver
- Ee-fu Noodles with Pork Liver
- Dry Bak Kut Teh with Liver
- Stir Fried Snow Pea with Lean Meat and Liver
- Stir Fried Pork and Kidney with Ginger and Sesame Oil
All of the organ meats are served less than 100g raw weight of liver and added to compliment the dishes. Nevertheless, even if you choose to omit pork liver in your confinement meals, there is nothing to significantly worry about as there is still adequate vitamin A from other animal sources like eggs, meat, and fish as well. Flexibility and individualizing perks is definitely something you want to check out in a confinement food delivery service.







